 爬虫工作的基本原理就是,给定一个初始的url,下载这个url的网页,然后找出网页上所有满足下载要求的链接,然后把这些链接对应的url下载下来,然后再找下载下来的这些网页的url,我们可以用广度优先搜索实现这个算法,不过,首先得有一个函数找出网页上所有的满足要求的url,下面这个例子用正则表达式找出url.
爬虫工作的基本原理就是,给定一个初始的url,下载这个url的网页,然后找出网页上所有满足下载要求的链接,然后把这些链接对应的url下载下来,然后再找下载下来的这些网页的url,我们可以用广度优先搜索实现这个算法,不过,首先得有一个函数找出网页上所有的满足要求的url,下面这个例子用正则表达式找出url.
最后就是广度优先搜索了,这个实现起来也很简单:
 作者用上面的算法,感觉速度还行,1小时可以抓10000多网页,可以满足小型系统的要求。
作者用上面的算法,感觉速度还行,1小时可以抓10000多网页,可以满足小型系统的要求。
保福寺研究僧
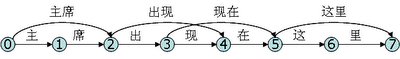 从而,找出这个句子的最短切分的问题就可以转化为找出上图的0-->7最短路径的问题。这里所有边的权值都是1。
从而,找出这个句子的最短切分的问题就可以转化为找出上图的0-->7最短路径的问题。这里所有边的权值都是1。
http://www.emacs.cn/Doc/CProgram
Emacs对于编辑程序有很多方便的功能,下面是在编辑C程序时常用到的一些功能。
一此有用的快捷键:
启动gdb调试器后,光标在源码文件缓冲区中时:
注:
jam -sBOOST_ROOT=. -sTOOLS=msvc "-sBUILD=debug release
以上命令解释如下:
-s 即set,设置环境变量;
BOOST_ROOT boost的存放目录
TOOLS 你选择的toolset,如gcc、msvc(即vc6)、vc7.1,此外还有gcc-stlport、msvc-stlport、vc7.1- stlport,表示同时使用stlport。具体支持何种toolset,大家可以自行到$BOOSTDIR\tools\build\v1看个究竟。 BUILD 编译类型,上述选项表示编译出支持static和dynamic链接的debug和release版本(4个版本)。
编译后的lib、dll将被copy到$BOOSTDIR\bin\boost\libs目录下,但是这些lib、dll分散在不同的目 录下,为了便于使用,可以在上述目录下分别查找*.lib和*.dll找出这些文件,然后将他们分别全部copy到VC的lib目录和Windows的 System32目录,也可以自己建立一个专门用于存放boost的lib文件的目录,然后 依次选择Tools->Options->Directories->Library files,将上述目录路径添加到VC的环境设置中。
到$BOOSTDIR下执行以下命令:
jam -sBOOST_ROOT=. -sTOOLS=gcc "-sBUILD=debug release
但建议用如下命令:
jam -sBOOST_ROOT=. -sTOOLS=gcc "-sBUILD=release
这样可以极大加快编译的速度,同时,个人认为像boost这样大的库,最好还是采用动态链接以减小目标程序的size,就像libstdc++,还没有见过有人去静态链接libstdc++.a,虽然系统中提供了这个静态库。

The solution is to use the CFLAGS, CPPFLAGS and LDFLAGS environment variables at configure time. For example, if you have ffmpeg library in one you your own directories, you can do (all on one command line):
./configure CFLAGS=-I/where/is/ffmpeg/include CPPFLAGS=-I/where/is/ffmpeg/include LDFLAGS=-L/where/is/ffmpeg/lib
If OpenCV is installed in a standard path, you can quickly compile all the C samples with:
cd /where/you/have/the/c/samples
sh ./build_all.sh
If OpenCV is not installed in a standard path, you need to setup the PKG_CONFIG_PATH variable. For example (assuming you are using a sh-based shell, like bash or zsh):
cd /where/you/have/the/c/samples
PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/where/you/have/installed/opencv/lib/pkgconfig:${PKG_CONFIG_PATH}
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH
sh ./build_all.sh
You can check that the PKG_CONFIG_PATH is correct by doing either:
pkg-config --cflags opencv
pkg-config --libs opencv
You must have something like:
$ pkg-config --cflags opencv
-I/where/you/have/installed/opencv/include/opencv
$ pkg-config --libs opencv
-L/com/softs/opencv-cvs/cvs-dev-i686/lib -lcxcore -lcv -lhighgui -lcvaux
The best way is to use pkg-config. Just define the correct PKG_CONFIG_PATH:
PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/where/you/have/installed/opencv/lib/pkgconfig:${PKG_CONFIG_PATH}
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH
And then, compile your program like:
gcc `pkg-config --cflags opencv` `pkg-config --libs opencv` -o my-opencv-prgm my-opencv-prgm.c
or simply:
gcc `pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv` -o my-opencv-prgm my-opencv-prgm.c
if that fails try:
gcc -I/home/intel/opencv/include -L/home/intel/opencv/lib -lopencv -lhighgui -lstdc++ opencv0.c -o opencv0
If, after following the instructions above, your program compiles, but gives an error message that a library cannot be found when it is run, on Fedora systems:
create a file called opencv.conf in /etc/ld.so.conf.d/ which contains the path to your opencv libraries (by default /usr/local/lib).
become root and run ldconfig.